Line Sizing Calculation (Part 1)
1.1. Flow Rate, Temperature and Pressure
Flow rate, pressure, and temperature for all process lines
used for line sizing calculation will be taken from the material balance from
Process Flow Diagram.
1.2. Line Sizing Criteria
The criteria shown on
Table 1 will be used to determine the line size. Such criteria are based on the
engineering practice used to select the economic size of piping inside the
plant battery limit.
Items
|
|
1. Gas/Vapor Lines
|
Pressure Drop(3)
- DP per 100 m < 0.117 bar (P < 34.3 barg)
- DP per 100 m 0.117-0.274 bar (34.3 < P < 137.2 barg)
Velocity(1)
-Velocity
< 18.3 m/s
|
2. Liquid Lines
|
For
Continuous & Non Continuous Lines:
- DP
per 100 m < 0.9 bar (2)
-
Velocity: <4 .6="" m="" s="" sup="">(1)
|
3. Two Phase Line
Velocity(4)
-
Velocity 4.6-15.2 m/s
-
Velocity must below than Verosion
Note:(1) Recommended
Practice for Design and Installation of Offshore Production Platform Piping
System, API RP 14E.
(2) Flow of Fluids through Valves,
Fittings, and Pipe
(3) Norsok
Standard No. P-CR-001-Rev 2
(4) Surface
Production Operation Vol. 1
Table 1.
Line Sizing Criteria (Main Process Line)
3.4. Equations
3.4.1.
Liquid phase
Liquid velocity
can be determined from following equation:
where Q : liquid flow
rate, kg/hr
r :
liquid
density, kg/m3
d
: pipe ID, mm
n : mean velocity of flow, m/s
Pressure drop (DP,
kg/cm2/100 m) is determined by fanning equation from API 14E:
Where f : Moody friction factor
Q :
liquid flow rate, m3/hr
S :
liquid specific gravity, dimensionless (water=1)
d : inside
pipe diameter, mm
Reynolds number (Re) of flow in pipe is
calculated from the following equation:
Where d : inside pipe diameter, mm
n : mean velocity of flow, m/s
r : liquid density, kg/m3
m : viscosity, kg/m.s
Friction
factor is calculated based on the following Colebrook's equation (ref: Oil field processing of petroleum vol.1
If Re>2000, use equation :
Where f : Moody friction factor
e :
surface
roughness, mm
D :
internal
diameter, mm
Re : Reynolds number
3.4.2.
Gas phase
Actual gas velocity can be determined by:
where Qg : gas
flow rate, Std.m3/hr
T : temperature,
oK
P : pressure,
kg/cm2a
d : inside pipe diameter, mm
v : gas velocity, m2/sec
Z : gas compressibility factor,
dimensionless
For compressible fluid with total pressure drop less than
10% of its initial pressure, the pressure drop (DP, kg/cm2/100 m) is
calculated using equation from API 14E as follows:

……………….……….(6)
S : gas specific gravity at standard condition,
dimensionless
Qg : gas flow rate, std.m3/hr
Z : compressibility factor, dimensionless
T1
: flowing
temperature, oK
f : Moody friction factor, dimensionless
L : length of pipe, m
P1 : upstream pressure, kg/cm2a
d : inside pipe diameter, mm
3.4.3. Gas/liquid
Two-phase
The fluid erosional velocity (Ve, m/s) is calculated using the following equation (API
14E):
Total weight flow of fluids is the sum of weight flow of
gas and weight flow of liquid. Weight flow of gas can be calculated by equation
below:
……………………....…….(8)
Where:
Gas flow :
mass gas flow (kg/s)
Qg : volumetric volume of gas, Std
m3/hr
Sg :
gas specific gravity
Note: standard gas volume 0.024 m3/gmole is
taken at pressure 1 atm and temperature 15oC
Weight flow of liquid can be calculated by
equation below:
Liquid
flow : mass liquid flow (kg/s)
Ql : volumetric volume of
condensate, m3/hr
Sl : gas
specific gravity
Total
fluid mass flow is the sum of gas flow and liquid flow:
…..…………....(10)
The total volume flow would be:
….……..……...(11)
Where
:
Volume
flow : volumetric flow, m3/s
Total
flow : fluid mass
flow, kg/s
rmixture : gas/liquid mixture density, kg/m3
Mixture velocity could be determined from following
equation:
Where :
V : velocity, m/s
d : inside diameter of pipe, mm
The pressure drop (DP,
kg/cm2/100m) in a two-phase steel piping system is estimated using
simplified Darcy equation (API 14E):
………………………..…(13)
f : Moody friction factor, dimensionless
d : inside pipe diameter, mm
rm : gas/liquid mixture density, kg/m3
W : total liquid plus vapor rate, kg/h
Please go to part 2 for example of calculation .

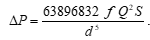











Komentar
Posting Komentar